The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is awarding $2 billion for 38 projects aimed at protecting the U.S. power grid against growing threats of extreme weather, lower costs for communities and increase grid capacity to meet load growth stemming from an increase in manufacturing, data centers and electrification.
The selected projects announced today through the Grid Resilience and Innovation Partnerships (GRIP) program will deploy transmission and distribution infrastructure and technology upgrades to enable 7.5 GW of grid capacity, speed up interconnection for new clean energy projects and catalyze $4.2 billion in public and private investment.
These projects, spanning 42 states and the District of Columbia, include the six projects across the Southeast, including utilities that were impacted by Hurricanes Helene and Milton.
The selected projects are slated to upgrade 950 miles of transmission by constructing more than 300 miles of new transmission lines and reconductoring or adding grid-enhancing technologies to 650 miles of transmission lines to increase the capacity of existing lines.
“The devastating and deadly hurricanes, Helene and Milton, have put on stark display how extreme weather events continue to stress the nation’s aging electric systems; but across the country, the Biden-Harris Administration is using every tool in the toolbox to make sure America’s power grid is hardened in the face of this challenge,” says U.S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer M. Granholm.
“The Administration’s Investing in America agenda has provided the largest grid investment in U.S. history helping us add more energy to the grid faster, improve reliability and resilience and invest in innovative technologies so customers across the country can have access to more renewable energy and pay less for their electricity.”
Funded by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, the GRIP program is investing $10.5 billion in communities across the country to enhance grid flexibility and improve the resilience of the power system against growing threats of extreme weather and climate change. The first round of GRIP funding, announced last October, included $3.5 billion for 58 projects in 44 states.
In August, DOE announced an additional $2.2 billion for eight additional selections. With these most recent selections, GDO has now announced a cumulative $7.6 billion in Federal funding for 104 projects through the GRIP program.
In total, GRIP projects are expected to enable 55 GW of grid capacity. The projects announced last October and this past August will upgrade an additional 1,650 miles of transmission.
Selected projects that will improve reliability and resilience include:
- Arizona: With the risk of wildfires increasing in the Southwest, Arizona Public Service Company (APS) will upgrade system devices, monitoring systems, upgrade wood utility poles and implement microgrids in vulnerable areas to enhance energy reliability and resilience for 289,000 meters customers. Approximately 69% of the project will be carried out in rural, Tribal or disadvantaged communities and APS estimates it will prevent nearly one million customer interruptions and save $113 million in emergency repair costs.
- Indiana and Illinois: Hoosier Energy Rural Electric Cooperative and Southern Illinois Power Cooperative will build new transmission feeds to loop transmission to 10 substations in seven counties. These substations face increasing outages from extreme weather events and tornados. Adding looped transmission will increase grid resilience and reduce outages by providing backup connections to additional substations.
- North Carolina: Randolph Electric Membership Corporation (REMC) will deploy a suite of grid system upgrades to improve service reliability and resilience within REMC’s system, support targeted grid modernization improvements and reduce outage duration while providing direct benefits to rural and underserved communities in North Carolina. The hardened grid will reduce outages from severe weather events for 32,000 customers in an area vulnerable to hurricanes. The area was affected by Winter Storm Finn in 2024 and Hurricane Ian in 2022.
- Texas: Entergy Texas will enhance grid resilience in disadvantaged communities in Port Arthur, Texas by fortifying critical infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events, which have historically caused significant power disruptions. The project will improve grid reliability, with expected savings of $74 million over 50 years by reducing power interruptions and reducing restoration costs.
Highlights of announced projects expected to increase grid capacity include:
- Alabama, Georgia, Kentucky, Missouri, North Carolina, Tennessee and Virginia: The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) and its project partners will conduct 84 resilience sub-projects across eight states to add 2,400 MW of transmission grid capacity, reduce TVA’s solar interconnection queue and reduce outage time. This project will create the first interconnection tie between TVA and the Southwest Power Pool, providing TVA and local power companies with 800 MW of new energy supply. The project will provide an anticipated 94% reduction in localized outage durations and provide 360 disadvantaged communities with an estimated $250 million in economic benefit.
- Massachusetts: Boston-based GridUnity will deploy software to improve the efficiency of the interconnection process with multiple Regional Transmission Organizations covering approximately 70% of the U.S. population to enhance energy reliability, security and lower costs. DOE’s Transmission Interconnection Roadmap found that interconnection queue delays “significantly delay clean energy deployment and lead to higher costs for project developers and electricity consumers.” By modernizing the interconnection process, the project will significantly reduce the time required to review, approve and commission new generation interconnections across the country and accelerate the approval of generation projects and grid developments that could employ 51,300 skilled workers.
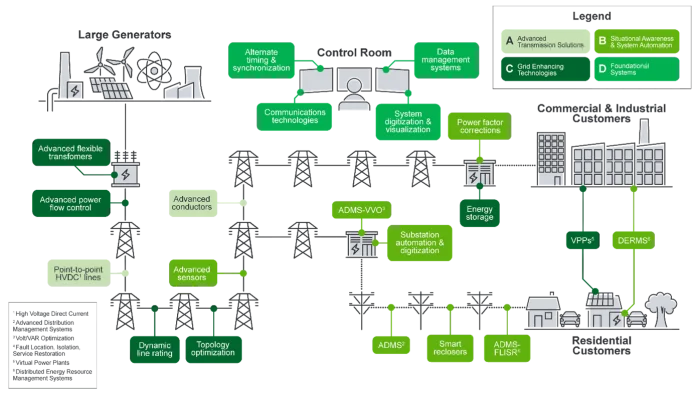
DOE’s Pathways to Commercial Liftoff: Innovative Grid Deployment report identified multiple advanced grid solutions that are commercially available today to enhance grid capacity, including advanced transmission and grid-enhancing technologies used in many of these projects. GRIP projects that align with report findings include:
- Connecticut: Elevate Renewables will reconfigure an existing fossil-fueled peaking generating station in Milford, Conn., integrating a 20 MW battery energy storage system to create a carbon-neutral synchronous condensing solution, or “green sync.” With 1,000 combustion turbine sites across the United States, the project has potential to be scaled nationwide.
- Georgia: Led by Georgia Transmission Corporation, a consortium of 12 not-for-profit rural utilities in 11 states will build, rebuild or reconductor transmission infrastructure to improve resilience and increase electric transfer capacity by deploying advanced overhead conductors.
Award negotiations will begin immediately. DOE expects to launch a third round of GRIP funding next year.